Page Not Found
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Page not found. Your pixels are in another canvas.
About me
This project studied the potential of Big data to inform destination management organizations. To do so, three sources of Big data are discussed: Telecom, Social media and Airbnb data. This is done through the demonstration and analysis of a set of visualizations and tools, as well as a discussion of applications and recommendations for challenges that have been identified in the market.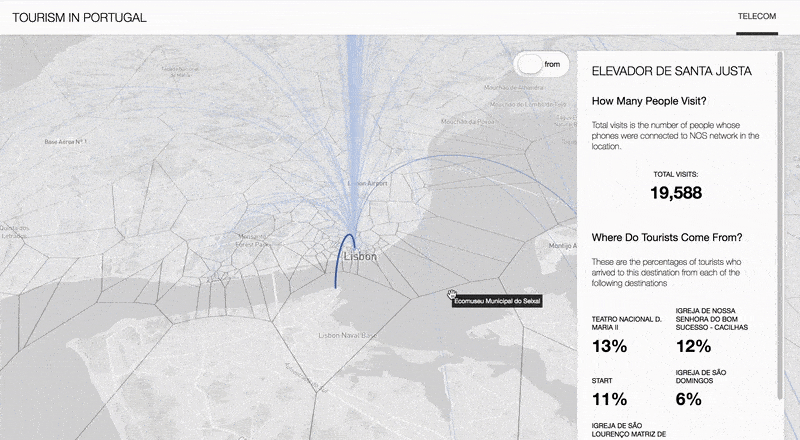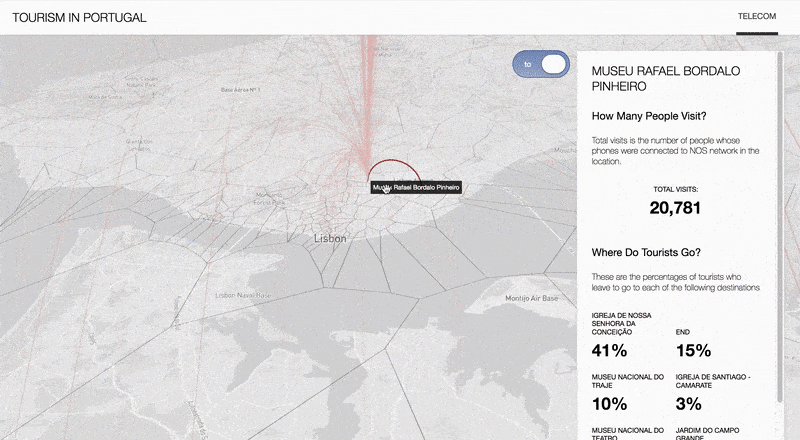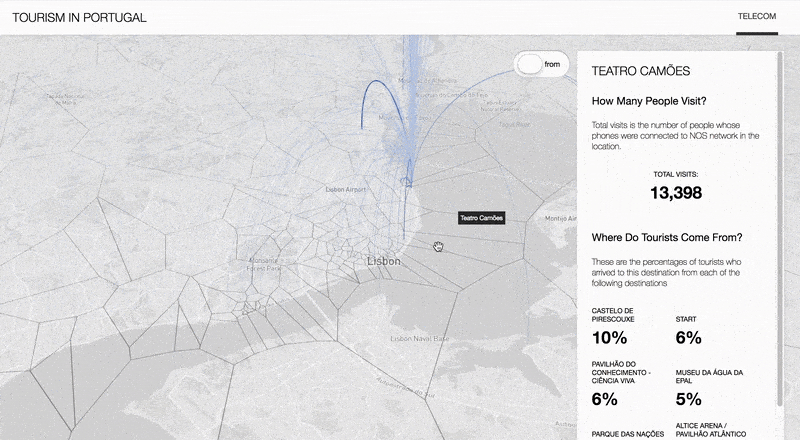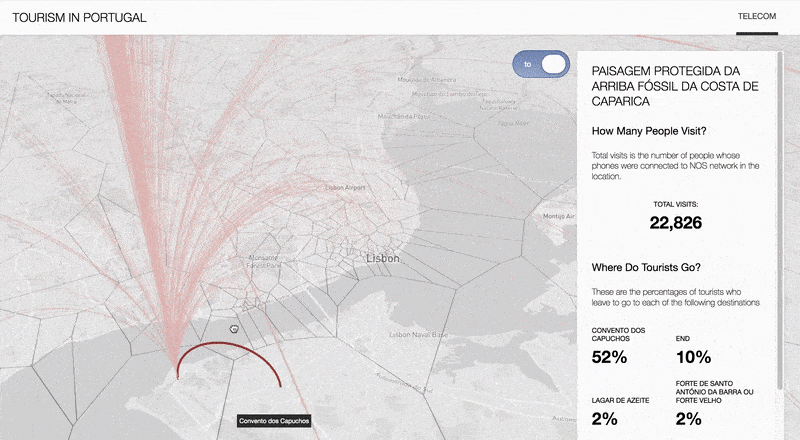
This project focused on the exploration of several machine learning (ML) techniques, covering different stages of a Land Use/Land Cover Classification (LULC) pipeline. These techniques aimed to minimise problems typically found in this kind of data, namely data ingestion, feature selection, data filtering and classification. This work was a joint effort between me and Manvel Khudinyan. 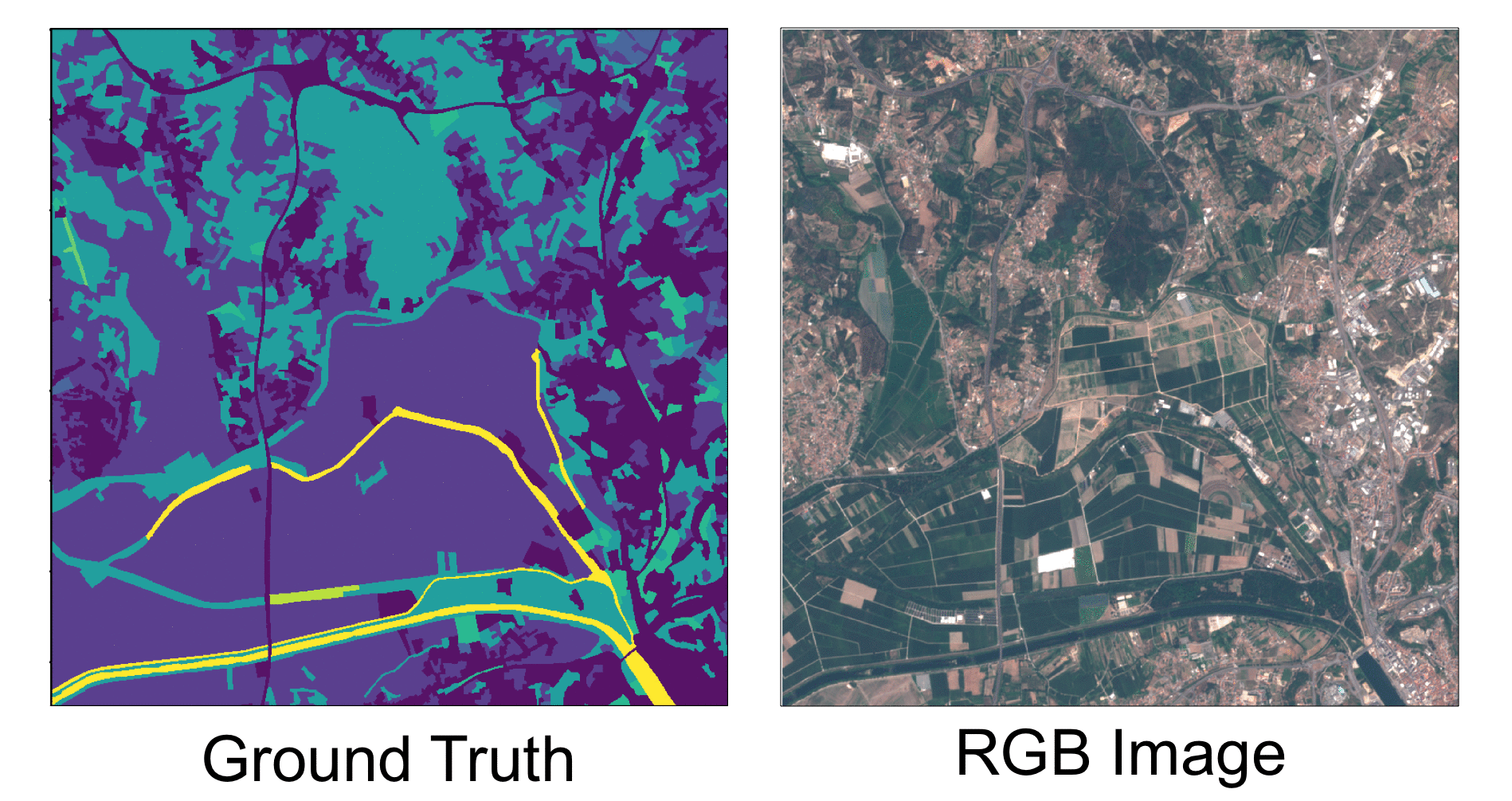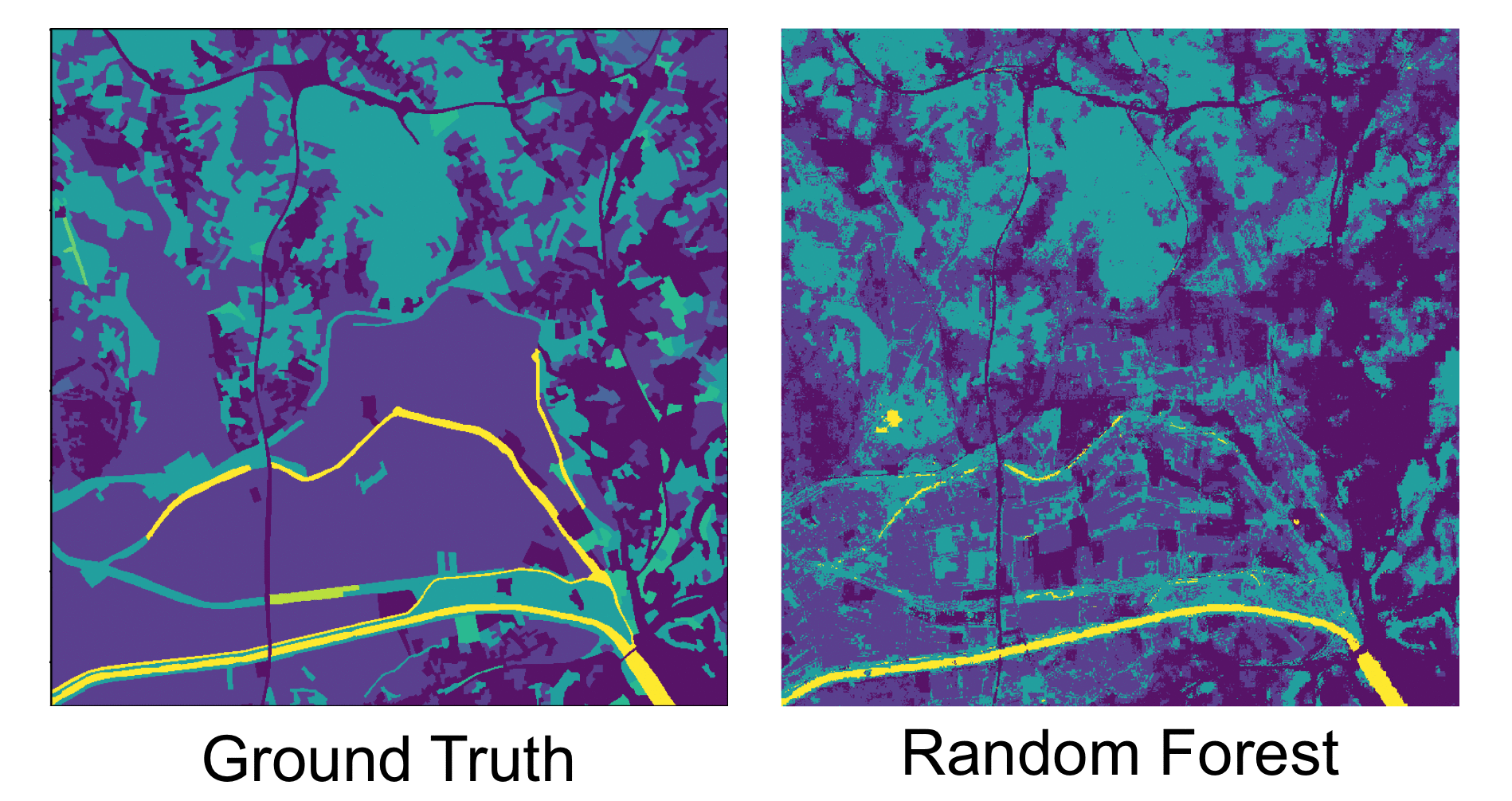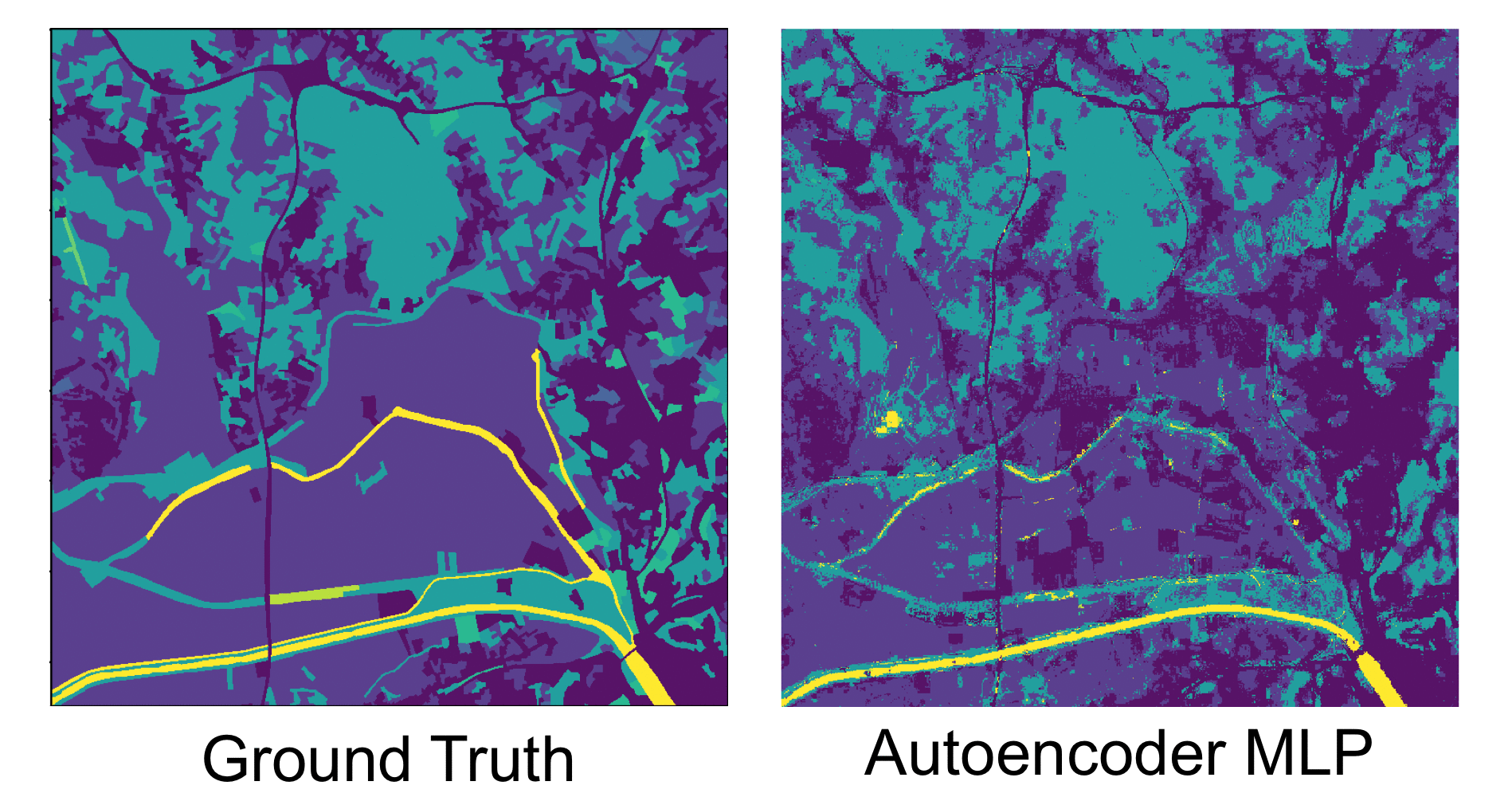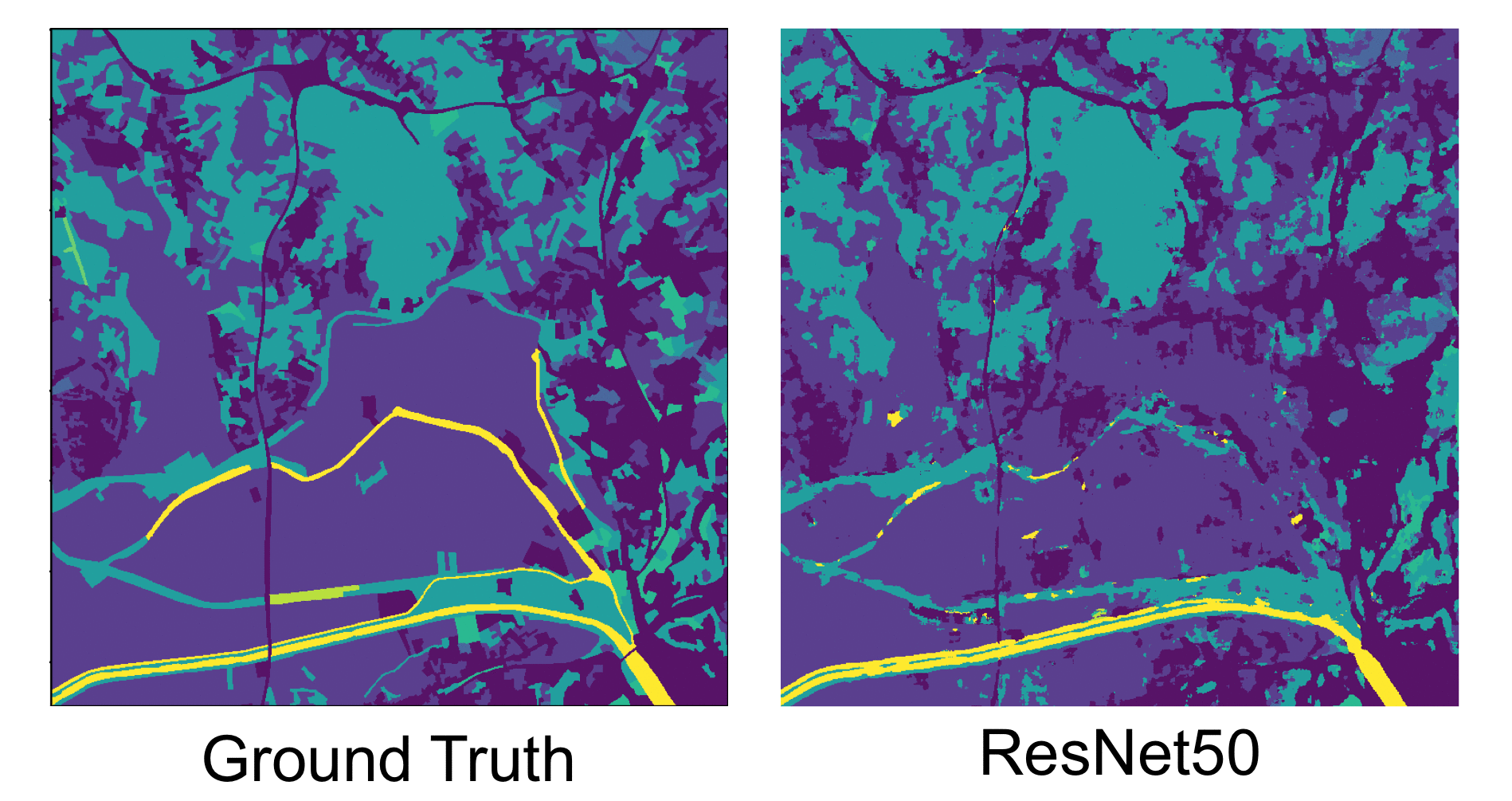
Cyclone Amphan made landfall in South Asia on May 20, 2020. It was the most damaging storm in the history of the Indian Ocean, rendering hundreds of thousands of people homeless, ravaging agricultural lands and causing billions of dollars in damage. How were people affected by the storm? What were the responses of individuals, governments, corporates and NGOs? How was it covered by local, national and international media, as opposed to individuals’ accounts? Who has created the dominant narratives of Cyclone Amphan; and whose voices go unheard? We aim to use online data – such as Twitter posts, news headlines and research publications – to analyze people’s experiences of Cyclone Amphan.
The competition’s aim was to optimize a keyboard layout to minimize the workload for usage by an ALS patient. Anthony Carbajal inspired this challenge, a full-time daily life hacker that aims to find innovative ways to improve his and other ALS-patient lives, with whom NILG.AI worked together for developing a first version of this solution. 
This project aims to develop a Competitive Intelligence platform through Natural Language Processing and various visualization techniques. We employ text preprocessing and embedding techniques to encode a large corpus of text as well as Self-Organizing Maps, an unsupervised neural network that facilitates the development of multiple machine learning tasks and visualize high dimensional data.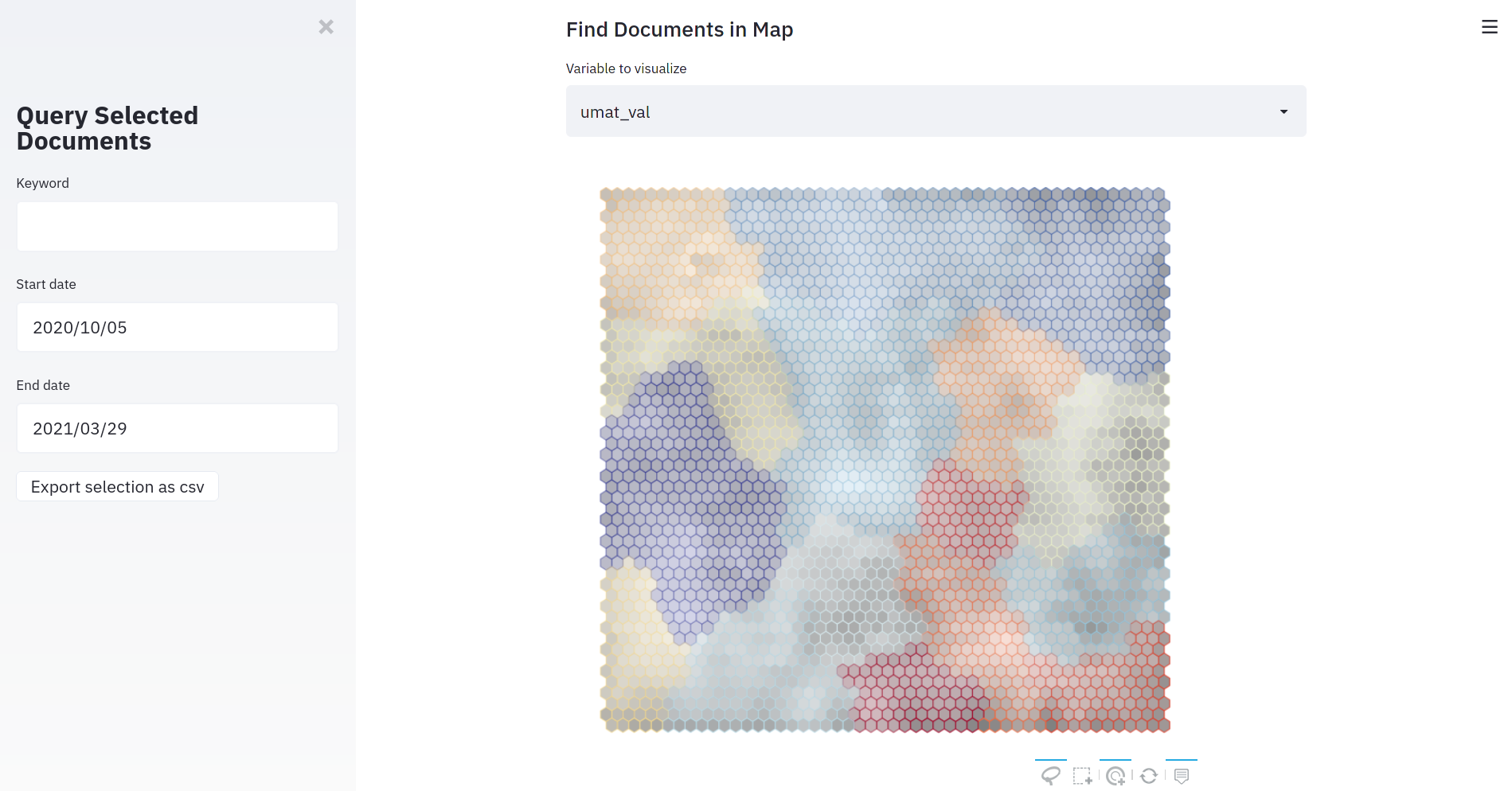
ML-Research contains the software implementation of most algorithms used or developed in my research. Specifically, it contains scikit-learn compatible implementations for Active Learning, Oversampling, Datasets and various utilities to assist in experiment design and results reporting. Other techniques, such as self-supervised learning and semi-supervised learning are currently under development and are being implemented in pytorch and intended to be scikit-learn compatible.
This project studies the importance of time in the reliability of algorithmic recourse. We highlight the lack of reliability in recourse recommendations over several competitive settings, potentially setting misguided expectations that could result in detrimental outcomes. These findings emphasize the importance of meticulous consideration when AI systems offer guidance in dynamic environments. Our paper, “Setting the Right Expectations: Algorithmic Recourse Over Time”, won the Best AI Track Paper award at EAAMO’23! 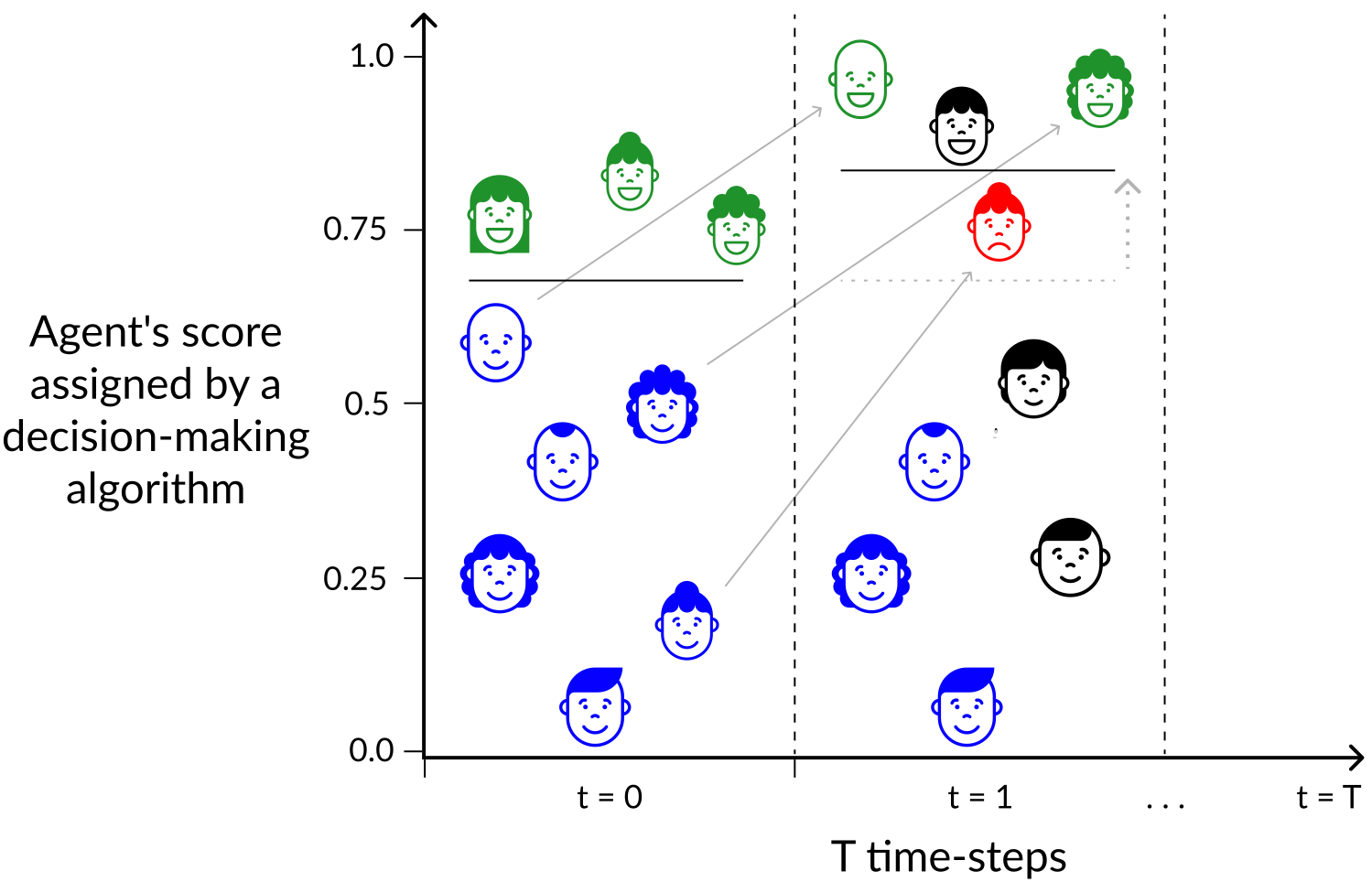
Douzas, G., Bacao, F., Fonseca, J., & Khudinyan, M. (2019). Imbalanced Learning in Land Cover Classification: Improving Minority Classes’ Prediction Accuracy Using the Geometric SMOTE Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 11(24), 3040.
The automatic production of land use/land cover maps continues to be a challenging problem, with important impacts on the ability to promote sustainability and good resource management. The ability to build robust automatic classifiers and produce accurate maps can have a significant impact on the way we manage and optimize natural resources. The difficulty in achieving these results comes from many different factors, such as data quality and uncertainty. In this paper, we address the imbalanced learning problem, a common and difficult conundrum in remote sensing that affects the quality of classification results, by proposing Geometric-SMOTE, a novel oversampling method, as a tool for addressing the imbalanced learning problem in remote sensing. Geometric-SMOTE is a sophisticated oversampling algorithm which increases the quality of the instances generated in previous methods, such as the synthetic minority oversampling technique. The performance of Geometric-SMOTE, in the LUCAS (Land Use/Cover Area Frame Survey) dataset, is compared to other oversamplers using a variety of classifiers. The results show that Geometric-SMOTE significantly outperforms all the other oversamplers and improves the robustness of the classifiers. These results indicate that, when using imbalanced datasets, remote sensing researchers should consider the use of these new generation oversamplers to increase the quality of the classification results.
Crayton A, Fonseca J, Mehra K, Ng M, Ross J, Sandoval-Castañeda M, von Gnecht R. (2021). Narratives and Needs: Analyzing Experiences of Cyclone Amphan Using Twitter Discourse, in IJCAI 2021 Workshop on AI for Social Good.
People often turn to social media to comment upon and share information about major global events. Accordingly, social media is receiving increasing attention as a rich data source for understanding people's social, political and economic experiences of extreme weather events. In this paper, we contribute two novel methodologies that leverage Twitter discourse to characterize narratives and identify unmet needs in response to Cyclone Amphan, which affected 18 million people in May 2020.
Fonseca, J., Douzas, G., Bacao, F. (2021). Improving Imbalanced Land Cover Classification with K-Means SMOTE: Detecting and Oversampling Distinctive Minority Spectral Signatures. Information, 12(7), 266.
Land cover maps are a critical tool to support informed policy development, planning, and resource management decisions. With significant upsides, the automatic production of Land Use/Land Cover maps has been a topic of interest for the remote sensing community for several years, but it is still fraught with technical challenges. One such challenge is the imbalanced nature of most remotely sensed data. The asymmetric class distribution impacts negatively the performance of classifiers and adds a new source of error to the production of these maps. In this paper, we address the imbalanced learning problem, by using K-means and the Synthetic Minority Oversampling TEchnique (SMOTE) as an improved oversampling algorithm. K-Means SMOTE improves the quality of newly created artificial data by addressing both the between-class imbalance, as traditional oversamplers do, but also the within-class imbalance, avoiding the generation of noisy data while effectively overcoming data imbalance. The performance of K-means SMOTE is compared to three popular oversampling methods (Random Oversampling, SMOTE and Borderline-SMOTE) using seven remote sensing benchmark datasets, three classifiers (Logistic Regression, K-Nearest Neighbors and Random Forest Classifier) and three evaluation metrics using a 5-fold cross-validation approach with 3 different initialization seeds. The statistical analysis of the results show that the proposed method consistently outperforms the remaining oversamplers producing higher quality land cover classifications. These results suggest that LULC data can benefit significantly from the use of more sophisticated oversamplers as spectral signatures for the same class can vary according to geographical distribution.
Fonseca, J., Douzas, G., Bacao, F. (2021). Increasing the Effectiveness of Active Learning: Introducing Artificial Data Generation in Active Learning for Land Use/Land Cover Classification. Remote Sensing, 13(13), 2619.
In remote sensing, Active Learning (AL) has become an important technique to collect informative ground truth data "on-demand" for supervised classification tasks. In spite of its effectiveness, it is still significantly reliant on user interaction, which makes it both expensive and time consuming to implement. Most of the current literature focuses on the optimization of AL by modifying the selection criteria and the classifiers used. Although improvements in these areas will result in more effective data collection, the use of artificial data sources to reduce human-computer interaction remains unexplored. In this paper, we introduce a new component to the typical AL framework, the data generator, a source of artificial data to reduce the amount of user-labeled data required in AL\@. The implementation of the proposed AL framework is done using Geometric SMOTE as data generator. We compare the new AL framework to the original one using similar acquisition functions and classifiers over three AL-specific performance metrics in seven benchmark datasets. We show that this modification of the AL framework significantly reduces cost and time requirements for a successful AL implementation in all of the datasets used in the experiment.
Fonseca, J., & Bacao, F. (2022). Research Trends and Applications of Data Augmentation Algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2207.08817.
In the Machine Learning research community, there is a consensus regarding the relationship between model complexity and the required amount of data and computation power. In real world applications, these computational requirements are not always available, motivating research on regularization methods. In addition, current and past research have shown that simpler classification algorithms can reach state-of-the-art performance on computer vision tasks given a robust method to artificially augment the training dataset. Because of this, data augmentation techniques became a popular research topic in recent years. However, existing data augmentation methods are generally less transferable than other regularization methods. In this paper we identify the main areas of application of data augmentation algorithms, the types of algorithms used, significant research trends, their progression over time and research gaps in data augmentation literature. To do this, the related literature was collected through the Scopus database. Its analysis was done following network science, text mining and exploratory analysis approaches. We expect readers to understand the potential of data augmentation, as well as identify future research directions and open questions within data augmentation research.
Fonseca, J., & Bacao, F. (2023). Improving Active Learning Performance through the Use of Data Augmentation. International Journal of Intelligent Systems, 2023.
Active learning (AL) is a well-known technique to optimize data usage in training, through the interactive selection of unlabeled observations, out of a large pool of unlabeled data, to be labeled by a supervisor. Its focus is to find the unlabeled observations that, once labeled, will maximize the informativeness of the training dataset, therefore reducing data-related costs. The literature describes several methods to improve the effectiveness of this process. Nonetheless, there is a paucity of research developed around the application of artificial data sources in AL, especially outside image classification or NLP. This paper proposes a new AL framework, which relies on the effective use of artificial data. It may be used with any classifier, generation mechanism, and data type and can be integrated with multiple other state-of-the-art AL contributions. This combination is expected to increase the ML classifier’s performance and reduce both the supervisor’s involvement and the amount of required labeled data at the expense of a marginal increase in computational time. The proposed method introduces a hyperparameter optimization component to improve the generation of artificial instances during the AL process as well as an uncertainty-based data generation mechanism. We compare the proposed method to the standard framework and an oversampling-based active learning method for more informed data generation in an AL context. The models’ performance was tested using four different classifiers, two AL-specific performance metrics, and three classification performance metrics over 15 different datasets. We demonstrated that the proposed framework, using data augmentation, significantly improved the performance of AL, both in terms of classification performance and data selection efficiency (all the codes and preprocessed data developed for this study are available at https://github.com/joaopfonseca/publications/).
Fonseca, J., & Bacao, F. (2023). Geometric SMOTE for imbalanced datasets with nominal and continuous features. Expert Systems with Applications, 234, 121053.
Imbalanced learning can be addressed in 3 different ways: resampling, algorithmic modifications and cost-sensitive solutions. Resampling, and specifically oversampling, are more general approaches when opposed to algorithmic and cost-sensitive methods. Since the proposal of the Synthetic Minority Oversampling TEchnique (SMOTE), various SMOTE variants and neural network-based oversampling methods have been developed. However, the options to oversample datasets with nominal and continuous features are limited. We propose Geometric SMOTE for Nominal and Continuous features (G-SMOTENC), based on a combination of G-SMOTE and SMOTENC. Our method modifies SMOTENC's encoding and generation mechanism for nominal features while using G-SMOTE's data selection mechanism to determine the center observation and k-nearest neighbors and generation mechanism for continuous features. G-SMOTENC's performance is compared against SMOTENC's along with two other baseline methods, a State-of-the-art oversampling method and no oversampling. The experiment was performed over 20 datasets with varying imbalance ratios, number of metric and non-metric features and target classes. We found a significant improvement in classification performance when using G-SMOTENC as the oversampling method. An open-source implementation of G-SMOTENC is made available in the Python programming language.
Fonseca, J., & Bacao, F. (2023). Tabular and latent space synthetic data generation: a literature review. Journal of Big Data, 10(1), 115.
The generation of synthetic data can be used for anonymization, regularization, oversampling, semi-supervised learning, self-supervised learning, and several other tasks. Such broad potential motivated the development of new algorithms, specialized in data generation for specific data formats and Machine Learning (ML) tasks. However, one of the most common data formats used in industrial applications, tabular data, is generally overlooked; Literature analyses are scarce, state-of-the-art methods are spread across domains or ML tasks and there is little to no distinction among the main types of mechanism underlying synthetic data generation algorithms. In this paper, we analyze tabular and latent space synthetic data generation algorithms. Specifically, we propose a unified taxonomy as an extension and generalization of previous taxonomies, review 70 generation algorithms across six ML problems, distinguish the main generation mechanisms identified into six categories, describe each type of generation mechanism, discuss metrics to evaluate the quality of synthetic data and provide recommendations for future research. We expect this study to assist researchers and practitioners identify relevant gaps in the literature and design better and more informed practices with synthetic data.
Fonseca, J.*, Bell, A.*, Abrate, C., Bonchi, F., & Stoyanovich, J. (2023). Setting the Right Expectations: Algorithmic Recourse Over Time. In Equity and Access in Algorithms, Mechanisms, and Optimization (pp. 1-11).
Algorithmic systems are often called upon to assist in high-stakes decision making. In light of this, algorithmic recourse, the principle wherein individuals should be able to take action against an undesirable outcome made by an algorithmic system, is receiving growing attention. The bulk of the literature on algorithmic recourse to-date focuses primarily on how to provide recourse to a single individual, overlooking a critical element: the effects of a continuously changing context. Disregarding these effects on recourse is a significant oversight, since, in almost all cases, recourse consists of an individual making a first, unfavorable attempt, and then being given an opportunity to make one or several attempts at a later date — when the context might have changed. This can create false expectations, as initial recourse recommendations may become less reliable over time due to model drift and competition for access to the favorable outcome between individuals. In this work we propose an agent-based simulation framework for studying the effects of a continuously changing environment on algorithmic recourse. In particular, we identify two main effects that can alter the reliability of recourse for individuals represented by the agents: (1) competition with other agents acting upon recourse, and (2) competition with new agents entering the environment. Our findings highlight that only a small set of specific parameterizations result in algorithmic recourse that is reliable for agents over time. Consequently, we argue that substantial additional work is needed to understand recourse reliability over time, and to develop recourse methods that reward agents’ effort.
Bell, A.*, Fonseca, J.*, Abrate, C., Bonchi, F., & Stoyanovich, J. (2024). Fairness in Algorithmic Recourse Through the Lens of Substantive Equality of Opportunity. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.16088.
Algorithmic recourse -- providing recommendations to those affected negatively by the outcome of an algorithmic system on how they can take action and change that outcome -- has gained attention as a means of giving persons agency in their interactions with artificial intelligence (AI) systems. Recent work has shown that even if an AI decision-making classifier is ''fair'' (according to some reasonable criteria), recourse itself may be unfair due to differences in the initial circumstances of individuals, compounding disparities for marginalized populations and requiring them to exert more effort than others. There is a need to define more methods and metrics for evaluating fairness in recourse that span a range of normative views of the world, and specifically those that take into account time. Time is a critical element in recourse because the longer it takes an individual to act, the more the setting may change due to model or data drift. This paper seeks to close this research gap by proposing two notions of fairness in recourse that are in normative alignment with substantive equality of opportunity, and that consider time. The first considers the (often repeated) effort individuals exert per successful recourse event, and the second considers time per successful recourse event. Building upon an agent-based framework for simulating recourse, this paper demonstrates how much effort is needed to overcome disparities in initial circumstances. We then proposes an intervention to improve the fairness of recourse by rewarding effort, and compare it to existing strategies.
Pliatsika, V., Fonseca, J., Wang, T., & Stoyanovich, J. (2024). ShaRP: Explaining Rankings with Shapley Values. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.16744.
Algorithmic decisions in critical domains such as hiring, college admissions, and lending are often based on rankings. Because of the impact these decisions have on individuals, organizations, and population groups, there is a need to understand them: to know whether the decisions are abiding by the law, to help individuals improve their rankings, and to design better ranking procedures. In this paper, we present ShaRP (Shapley for Rankings and Preferences), a framework that explains the contributions of features to different aspects of a ranked outcome, and is based on Shapley values. Using ShaRP, we show that even when the scoring function used by an algorithmic ranker is known and linear, the weight of each feature does not correspond to its Shapley value contribution. The contributions instead depend on the feature distributions, and on the subtle local interactions between the scoring features. ShaRP builds on the Quantitative Input Influence framework, and can compute the contributions of features for multiple Quantities of Interest, including score, rank, pair-wise preference, and top-k. Because it relies on black-box access to the ranker, ShaRP can be used to explain both score-based and learned ranking models. We show results of an extensive experimental validation of ShaRP using real and synthetic datasets, showcasing its usefulness for qualitative analysis.
Bell, A.*, Fonseca, J.*, & Stoyanovich, J. (2024). The Game Of Recourse: Simulating Algorithmic Recourse over Time to Improve Its Reliability and Fairness. In SIGMOD/PODS'24: Companion of the 2024 International Conference on Management of Data. ACM.
Algorithmic recourse, or providing recommendations to individuals who receive an unfavorable outcome from an algorithmic system on how they can take action and change that outcome, is an important tool for giving individuals agency against algorithmic decision systems. Unfortunately, research on algorithmic recourse faces a fundamental challenge: there are no publicly available datasets on algorithmic recourse. In this work, we begin to explore a solution to this challenge by creating an agent-based simulation called The Game of Recourse (an homage to Conway's Game of Life) to synthesize realistic algorithmic recourse data. We designed The Game of Recourse with a focus on reliability and fairness, two areas of critical importance in socio-technical systems.
Undergraduate course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA School of Business and Economics, 2018
Masters course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA Information Management School, 2019
Masters course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA School of Business and Economics, 2020
Masters course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA Information Management School, 2022
Masters course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA Information Management School, 2023
Undergraduate course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA Information Management School, 2023
Undergraduate course, Universidade NOVA de Lisboa, NOVA Information Management School, 2023