Imbalanced Learning in Land Cover Classification: Improving Minority Classes’ Prediction Accuracy Using the Geometric SMOTE Algorithm
Published in Remote Sensing, 2019
Douzas, G., Bacao, F., Fonseca, J., & Khudinyan, M. (2019). Imbalanced Learning in Land Cover Classification: Improving Minority Classes’ Prediction Accuracy Using the Geometric SMOTE Algorithm. Remote Sensing, 11(24), 3040. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11243040
Abstract
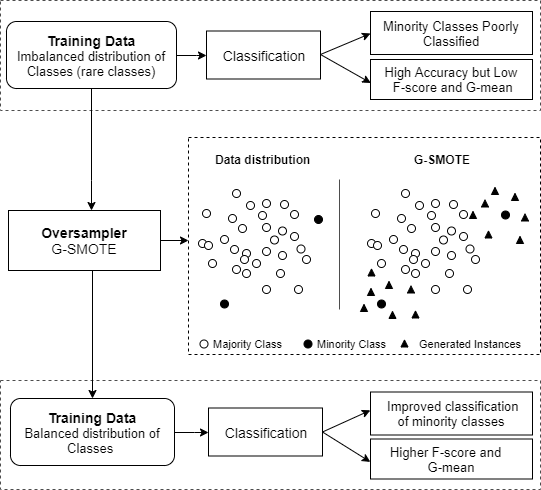
The automatic production of land use/land cover maps continues to be a challenging problem, with important impacts on the ability to promote sustainability and good resource management. The ability to build robust automatic classifiers and produce accurate maps can have a significant impact on the way we manage and optimize natural resources. The difficulty in achieving these results comes from many different factors, such as data quality and uncertainty. In this paper, we address the imbalanced learning problem, a common and difficult conundrum in remote sensing that affects the quality of classification results, by proposing Geometric-SMOTE, a novel oversampling method, as a tool for addressing the imbalanced learning problem in remote sensing. Geometric-SMOTE is a sophisticated oversampling algorithm which increases the quality of the instances generated in previous methods, such as the synthetic minority oversampling technique. The performance of Geometric-SMOTE, in the LUCAS (Land Use/Cover Area Frame Survey) dataset, is compared to other oversamplers using a variety of classifiers. The results show that Geometric-SMOTE significantly outperforms all the other oversamplers and improves the robustness of the classifiers. These results indicate that, when using imbalanced datasets, remote sensing researchers should consider the use of these new generation oversamplers to increase the quality of the classification results.
Graphical abstract is provided below: